Cytology
Basic Facts
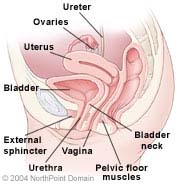
- Urine cytology refers to the study of cells that are shed from the inner lining of the urinary tract into the urine.
- This test is used primarily to identify cancers affecting the linings of the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra.
- One to 12 percent of patients may be given a “false positive” reading, suggesting that they have cancer when they do not.
Cytology is the study of cells from various body tissues and fluids to help diagnose disease. Urine cytology can help diagnose cancer and viral diseases. Urine cytology studies are useful in:
- Initial screening of patients with hematuria (blood in the urine); and
- Follow-up study of patients who have had previously treated superficial bladder cancer.
PRE-TEST GUIDELINES
No preparation is necessary prior to the test.
RISK FACTORS
There are no risk factors involved in a urine cytology test.
WHAT TO EXPECT
For this test, urine must be collected in one of two ways: the urine sample or the saline bladder wash. For the urine sample, patients urinate into a sterile container. For the saline bladder wash, a saline solution is flushed through the bladder through a catheter or a scope inserted into the urethra. The samples taken from the urine collection are sent to a lab for analysis, which may take 1 to 5 days.
POST-TEST GUIDELINES
Patients can resume normal activities immediately following the test.
Copyright © 2017 NorthPoint Domain, Inc. All rights reserved.
This material cannot be reproduced in digital or printed form without the express consent of NorthPoint Domain, Inc. Unauthorized copying or distribution of NorthPoint Domain’s Content is an infringement of the copyright holder’s rights.

