Digital Rectal Exam
Basic Facts
- A digital rectal examination detects abnormalities in the prostate gland and the colon.
- To screen men for prostate cancer, this test is best combined with a PSA test, or a laboratory analysis of how much of a prostate protein exists in a blood sample.
- All men should begin these screenings at ages 45 to 50.
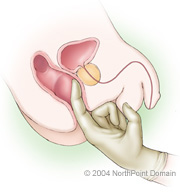
A digital rectal exam (DRE) is the manual examination of the prostate and rectal lining to feel for abnormalities, such as lumps or hard areas. A DRE can be conducted both on men and women for a variety of conditions, including colon cancer or problems in the urinary tract. However, urologists primarily perform DREs to screen men for an enlarged prostate.PRE-TEST GUIDELINES
No preparation is needed for a DRE. However, a patient should inform the physician if he or she has hemorrhoids or other rectal condition.
WHAT TO EXPECT
The physician instructs the patient to remove his or her clothing from the waist down. The patient is instructed to either lie on his or her side on the exam table or lean over the table, with his or her elbows on the table. The physician inserts a gloved, lubricated finger in the patient’s rectum to feel for abnormalities in the prostate and in the rectum.
POST-TEST GUIDELINES
Following the exam, if the physician suspects prostate cancer, he or she will order a biopsy for a definitive diagnosis.
POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
The patient may experience minor rectal bleeding if he or she has hemorrhoids.
Copyright © 2017 NorthPoint Domain, Inc. All rights reserved.
This material cannot be reproduced in digital or printed form without the express consent of NorthPoint Domain, Inc. Unauthorized copying or distribution of NorthPoint Domain’s Content is an infringement of the copyright holder’s rights.

